Monday, January 29, 2007 @ 8:17 PM
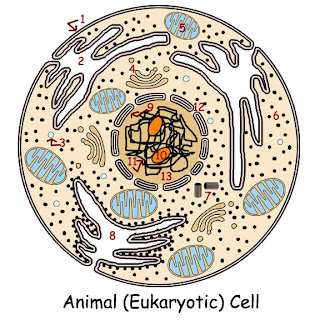
Plasma membrane
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Vacuole
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondrion
Ribosomes
Centrioles
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
--Parts of Nucleus--
Nuclear envelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear pore
- The plasma membrane, which serves as a diffusion barrier between the cell and its environment. A "diffusion barrier" prevents the loss of cellular materials by interfering with the physical tendency of molecules to spread out. It prevents substances from diffusing into the cell and also controls the movements of various substances and objects into and out of the cell.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) interconnects with the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. "Endo" means "inside," "plasmic" refers to the cytoplasm, and "reticulum" means, "network." It comes in two types--smooth and rough.
- Rough ER helps to compartmentalize the cell, and it serves as routes for the transport of materials from one part of the cell to another. It's associated with lipid synthesis and protein synthesis. It has ribosomes attached to its outer surface.
- Each cell contains Golgi apparatus. Their function is to process materials manufactured by the cell, then package those products into small structures called "Golgi vesicles." They contain materials, usually enzymes, which the cell needs, but which must remain packaged away from the cell's other contents.
- Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes, which, if released into the cell, would digest the vital components of the cell, and kill it. "Lysis" means "breakage," and "some" means "body."
- The other kind of Golgi vesicle contains materials to be exported from the cell. These materials are not waste products--they are chemicals intentionally manufactured by the cell for export.
- Mitochondria are very complex, double-membrane-bound organelles. Their function is to perform the aerobic portions of aerobic cellular respiration, the essential energy-producing process of the cell. Mitochondria contain their own naked, circular DNA and their own ribosomes.
- Ribosomes are to make protein, following instructions sent from the DNA's genes.
- The nucleus of the cell is a chamber specialized in DNA functions. A double layer of membrane called the nuclear envelope encloses it. The function of the nuclear envelope is to confine the materials necessary for DNA synthesis inside the nucleus, and controlling movement into and out of the nucleus.
- Assembly of ribosomes takes place in nucleolus, found in the nucleus.
- The nucleus contains a number of chromosomes, which are composed of DNA and histone proteins. Chromosomes carry the information archive of the cell. Each gene is a set of instructions for the construction of a specific protein.
- Nuclear pores perforate the double nuclear envelope. These pores do have structures in them that open and close to control movement through the pores. The nuclear pores are important for ribosomes to leave the nucleus. Though ribosomes are constructed in the nucleus, they must move to the cytoplasm in order to function.
- The nucleoplasm is substance that fills the interior of the nucleus. It is mostly composed of water, containing a complex assortment of materials. Nucleoplasm would be distinct from cytoplasm due to the high concentration of materials like nucleotides, which are used to make DNA, and the suite of enzymes, which control the DNA construction reactions.
Labels: Qn 1


